|
Memories
|
| |
Topics: |
Last updated:
19-03-13 |
| |
 |
ROM structures will be stored as LUT's (distributed ROMs) or
BlockRAMs without write signals |
 |
Static RAM (without clock signals) will use Flip/Flop's and hence be
"expencive" |
 |
Will be either LUT's (distributed memory) or Block RAM's |
 |
You may consider four ways to work with storage: Flip/Flops,
LUT's, BlockRAM and external RAM |
 |
Example of how RAM can useful in order to connect two systems with
different clock speeds. |
 |
Example of stored data (Waveform generator) |
| |
|
|
Exercises / Problems: |
|
|
| |
|
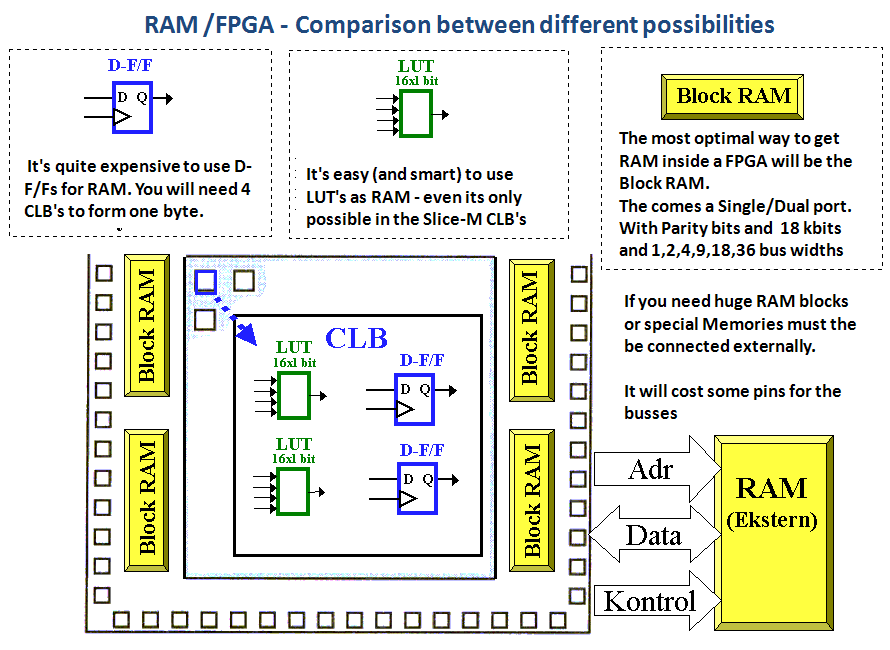
Simplified FPGA-model |
|
The model below was true in the
old Spartan 2 family |
| |
|
| |
- By using Flip/Flop's for storage
will you get a very flexible memory (in fact will
you be able to reach all memory cells in parallel -
but the price quite high.
- The LUT's will be useful as
distributed RAM/ROM - (at least in the Slice-M
portion of the CLB's)
- Block RAMs comes as single or
dual port with data busses like: 1-2-4-9-8-36 bits
- External RAM will normally be of
the static type (however does the new Spartan 6
offer drivers for dynamic RAM)
|
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Extract from the datasheet
for Spartan 3E |
|
Please note: The
CLB's inside a Spartan 3E FPGA made of four "Slices" and to make the
confusion total is a slice pretty much the same a CLB in the old
spartan 2 family.
The SLICEM can be uses for Logic purposes and also
as Memory (Distributed RAM) or Shift-register.
The SLICEL can be used for Logic only |
|
|
|
