CPU - The Gnome
|
| |
Topics: |
Last updated:
05-11-09 |
 |
To present a very
simple CPU - Lots of potential for enhancements
 |
To
present how new instructions and functionality can be added.
|
|
|
 |
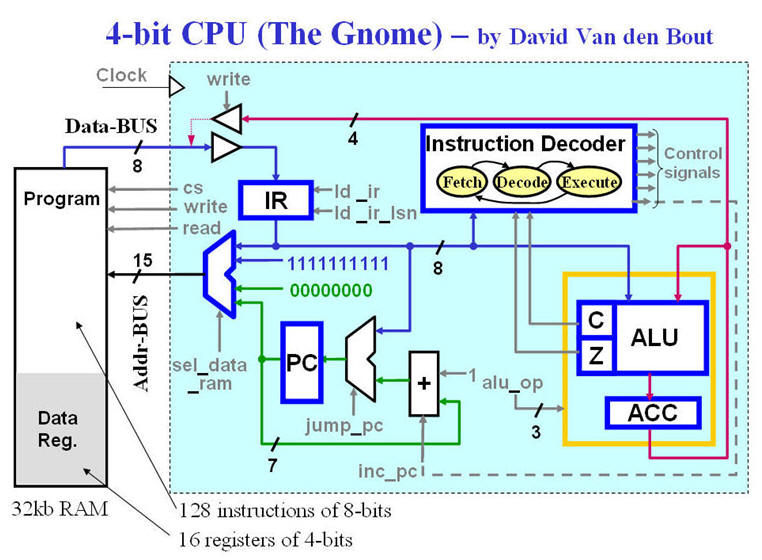
The "brain" of the Gnome actually a counter (
a State Machine with 3 states) which controls the registers and the
ALU |
 |
All CPUs born with ways of addressing data:
Immediate, Direct, Absolute, Relative and Inherent what it offers. |
 |
The Instruction set includes: Loading,
Storing, Addition, Test, XOR, Jump, Conditional Jump |
 |
The Memory divided in 128 byte program and
16x4-bit registers, The Address Multiplexer selects the wanted block |
 |
The Program Counter parts of all CPUs and will
always point at the next instruction. |
 |
The Instruction Register holds the instruction
(the Opcode) for execution. |
 |
The Brain of the CPU = A State Machine with
the states: Fetch, Decode and Execute. |
 |
The Calculator of the CPU - All Arithmetic and
Logic instructions are performed here under control of the
Instruction Decoder |
 |
This CPU will be based at pure Concurrent code
and Combinatorial Processes - Only one Clocked process |
 |
|
 |
A special designed Memory block for this FPGA
implementation of the Gnome. |
| |
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| Exercises
/ Problems: |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
